The field of Artificial Intelligence (AI) is flourishing thanks to large investments, and big companies with heavy ecological footprints can use it to make their activity more sustainable. This article focuses on multiple areas where AI can be helpful in achieving such goals.
—
What is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial Intelligence, or AI, as we call it refers to the ability of any machine or computer to mimic human capabilities such as learning from examples and experience, recognising objects, understanding and responding to language, making decisions, and solving problems. Combining these different capabilities, the machine can perform complex functions such as driving a car.
AI has gained popularity due to its successful deployment in applications that were once unthinkable —for instance, talking to Siri or Alexa to set up your calendar. Here are some illustrative examples of companies using AI to be more in line with a sustainable future.
- Google uses an AI model to reduce the energy load of its resource-hungry data centres, reducing the energy cost of cooling by 40%.
- IBM is using AI for better weather forecasting , making their predictions 30% more accurate. This helps renewable energy companies to better manage their plants, maximising renewable energy production, and reducing carbon emissions.
- Xcel Energy, a coal-burning and nitrous oxide-emitting utility company, is using AI to better predict energy consumption patterns and adapt its operating systems, thus significantly boosting efficiency (~20%).
- Carbon Tracker, a climate advocacy think-tank, uses AI to track emissions from coal plants using satellite imagery. Using satellite data they help guide investments toward lower-footprint ventures.
How AI Impacts Sustainable Development Goals
AI plays an important role in achieving not only environmental but all other Sustainable Development Goals- from ending hunger and poverty to achieving sustainable energy and gender equality to protecting and preserving biodiversity. The figures below illustrate the potential gains that can be realised in achieving SDG by adopting AI.
There are a total of 17 Sustainable Development Goals as defined by the United Nations, that can be grouped under three pillars: Environment, Economy and Society. A study published in Nature Communications looked at how the development of AI could enable many advances, while also hampering others.
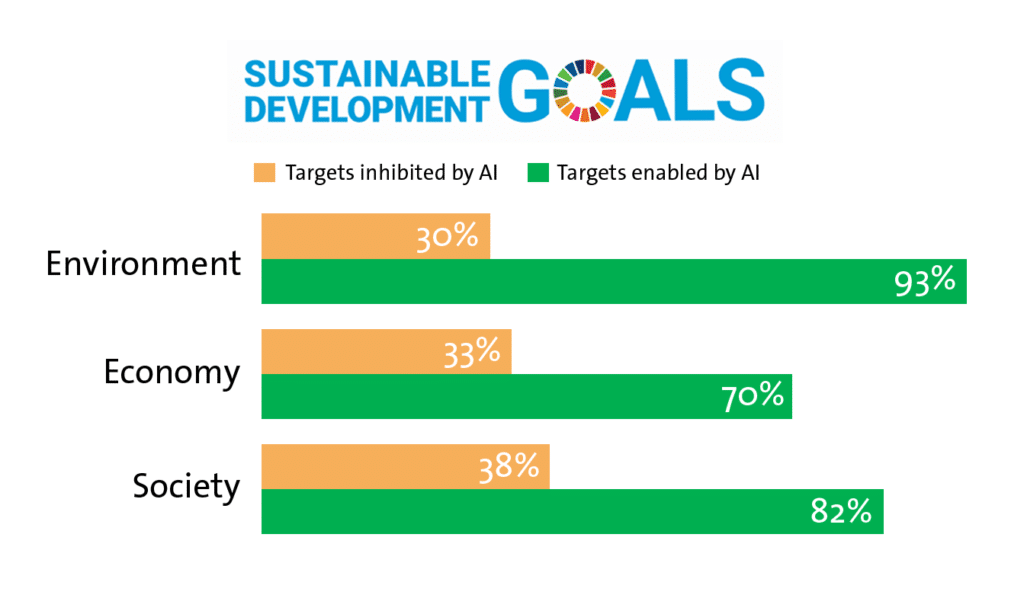
Figure1: Impact of AI on the achievement of each target from the Sustainable Development Goals. Source: Springer Nature Sustainability Community.
The takeaway is that, while AI provides unprecedented opportunities, these may not always result in a positive outcome depending on the framework in which they are used. For instance: a country with little ethical scrutiny, transparency and democratic measures could lead to AI enabling nationalism, discrimination and undemocratic election results. Better regulatory bodies need to be set up to oversee the development of AI, as its development will strongly influence the future of humanity.
AI to Address Environmental Challenges: Opportunities
AI has the potential to accelerate global efforts to protect the environment and conserve resources by detecting energy emission reductions, CO2 removal, helping develop greener transportation networks, monitoring deforestation, and predicting extreme weather conditions. Below mentioned are examples of how AI provides means to tackle the most pressing environmental challenges.
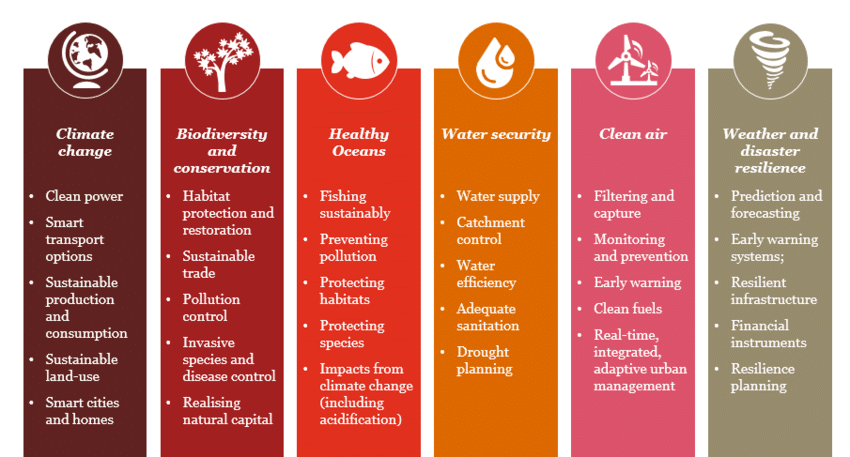
Figure 3: Priority action areas for environmental challenges; Image Source: PwC
Climate Change
- Use of machine learning to optimise energy generation and demand in real-time; better grid systems with increased predictability and increased efficiency, and use of renewable energy.
- Smart sensors and meters can be deployed within buildings to collect data and monitoring, analysing, and optimising energy usage in buildings.
- AI is already being used in smart transport eg: google maps and Waze, where Machine learning algorithms are used to optimise navigation; increase safety and provide information regarding traffic flows and congestion (e.g. Nexar).
Biodiversity and Conservation
- When combined with satellite imagery, AI can detect changes in land use, vegetation, forest cover, and the fallout of natural disasters.
- Invasive species can be monitored, identified and tracked using the technology above, identifying and tracking their presence, and eliminating them is all done using machine learning and computer vision. A company called Blue River Technology is using AI to detect the presence of invasive species and other biodiversity changes.
- Predictive softwares have been deployed to help anti-poaching units plan their patrol routes
Ocean Health
- AI can gather data from ocean locations that are hard or impossible to reach and thus, help protect species and habitats. Illegal fishing can also be tracked using AI.
- AI-powered robots can be used to monitor ocean conditions such as pollution levels, temperature and pH.
Water Issues
- AI is widely used by water scientists to project water usage in a particular geographical area and make weather forecasts to make informed policy decisions.
- AI along with satellite data can help to forecast weather, soil and subsurface water conditions and predict droughts.
Healthy Air
- Air purifiers with AI can record air quality and environmental data in real-time and adapt the filtration efficiency.
- AI-powered simulations can send warnings to people living in urban areas about the pollution levels of their areas. There are tools that can detect the pollution sources quickly and accurately.
- Using data from vehicles, radar sensors and cameras AI can help improve air pollution.
Weather forecast and Disaster resiliency
- AI-powered predictive analytics along with drones, advanced sensor platforms and similar tools can monitor tremors, floods, windstorms, sea-level changes, and other possible natural hazards. This technology can help government and concerned agencies to take timely actions and the availability of such information in real-time with automated triggers can enable early evacuations when needed.
- Various meteorological companies, tech companies like IBM, Palantir, and insurance companies are combining AI with traditional physics-based modelling methods to model the impact of extreme weather events on infrastructure and on their other systems to advise the disaster risk management strategies.
This article was written by Deeksha Chopra.
You might also like: 7 Data-Based & Artificial Intelligence Projects To Help Fight Climate Change









![The Statistics of Biodiversity Loss [2020 WWF Report]](https://u4d2z7k9.rocketcdn.me/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/lprwinkyTHB-544x306.jpg)





